Strengths and limitations of Photogrammetry
What is Photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry is the science of measuring real-world objects and terrain features from photographs. Imagery may be captured from cameras in the air (aerial) or on the ground (terrestrial).
How does it work?
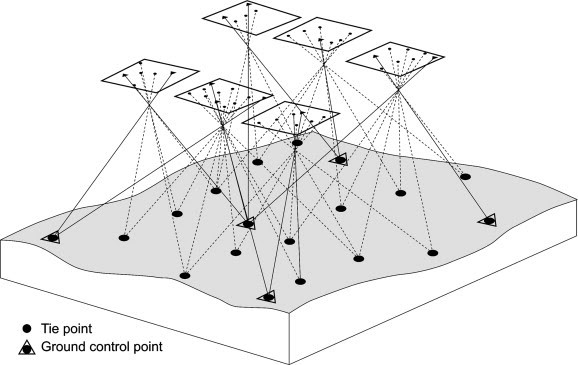
Photographs of an object are captured from different locations/angles.
The resulting ‘rays’ (representing the line of sight from the camera to a point on the object), are mathematically reconstructed to produce 3D coordinates of the point.
These 3D coordinates produce a digital model of the real-world object, allowing precise measurements of features.
What is it used for?
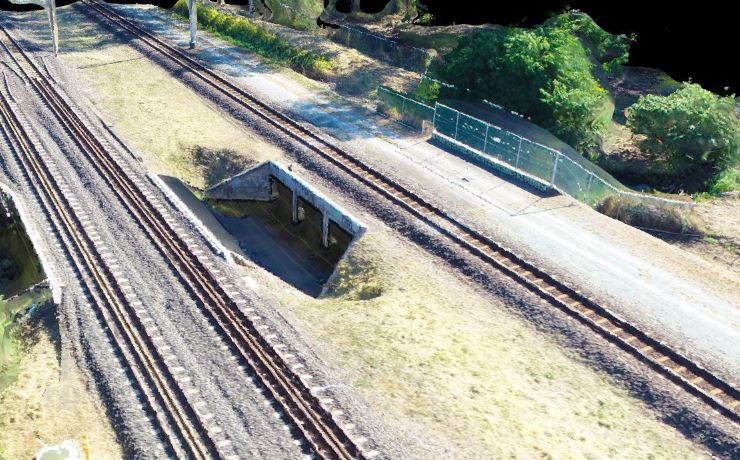

- To generate digital models of real-world objects
- To measure distances, heights, areas and volumes
- To prepare accurate topographic maps
+ Strengths of aerial photogrammetry
- Quick and cost-effective collection of data
- Highly accurate, reliable, quantifiable results
- Improved efficiency - one widely mapped area can be used for multiple analyses
- Provides an actual and permanent photographic record
- Easy to re-process data for new information without the need for expensive fieldwork to re-survey the area
- Ability to capture data in remote, unsafe or difficult to access locations, lowering safety risks
- Data acquisition can be done without disrupting operations on the ground and analysis can be performed from the office rather than in the field
- Full colour models and point clouds are easy to visualise and analyse
– Limitations of aerial photogrammetry
- Visibility constraints such as rain, fog, or dense vegetation cover can block the camera’s line of sight or limit light required for clear photography
- Poor weather conditions such as precipitation or wind can affect image capture and quality
- Altitude of flight required to achieve high image resolution and accuracy may be restricted by terrain or the built environment
- Difficulty matching points between images with low-contrast or uniformly textured surfaces e.g. sand, dense vegetation, short grass, tight crops, water bodies.
Why is it useful?
- Infrastructure planning and design
- Drainage analysis and flood mapping
- Volume calculations of stockpiles and landfill
- Environmental monitoring
Using drones for offers a cost-effective method of aerial data capture for photogrammetry compared with traditional methods involving full sized manned aircraft. Photogrammetry has many advantages when performed and used correctly, but understanding its strengths and limitations is essential to recognising when it is well suited for the requirements of a project or if an alternative method is more appropriate.
At Scout Aerial, we are committed to providing reliable, accurate and valuable insights using our wide-ranging experience and expertise. We partner with our clients to better understand their context and requirements to produce results that can be trusted and build relationships that last.
Related Articles: Aerial Surveys by drone, LiDAR or Photogrammetry?, RTK and PPK Drone Surveys
Contact us today to learn more.
References: Diagram